Agricen’s Scott Lay sat with Dennis Michelsen of WITY Radio to discuss where TITAN XC and EXTRACT PBA fit into fall practices, and how they can help farmers ensure that every dollar they spend on fertility inputs makes a bigger impact.
Agricen’s Scott Lay sat with Dennis Michelsen of WITY Radio to discuss where TITAN XC and EXTRACT PBA fit into fall practices, and how they can help farmers ensure that every dollar they spend on fertility inputs makes a bigger impact.
Dennis - WITY Radio: With the excellent yields that we've had the last few years, agronomists I’ve talked to say that we've taken more nutrients out of the soil than ever before, and that it's important to recharge those nutrients this fall.
Scott - Agricen: When yields are removed, nutrients are also removed from the soil profile, so it's important to replenish those. It also makes sense to utilize technologies that increase the availability of the nutrients that you've paid for. In a year like this one, with commodity prices diminished 15 to 20% relative to a year ago, every dollar counts. Given the economic scenario, the question of how to increase the amount of nutrients available to the crop next spring and summer becomes even more important.
Dennis - WITY Radio: Some local producers have told me “The only way I can make money this year is by growing more bushels.” So it doesn't really pay to cut back on your dry fertilizer game plan unless you can use a technology like TITAN XC to help you get more out of the dry fertilizers you're already applying.
Scott - Agricen: That's correct. We've had TITAN XC on the market since 2013. It’s a complement to traditional fertility practices. This fall, TITAN XC was applied on its 100 millionth-acre since introduction. With TITAN XC on dry fertilizer, we have a number of university studies that indicate we're increasing the first-year availability of phosphorus by 15 to 20% and potash by about 10%. So the value is there.
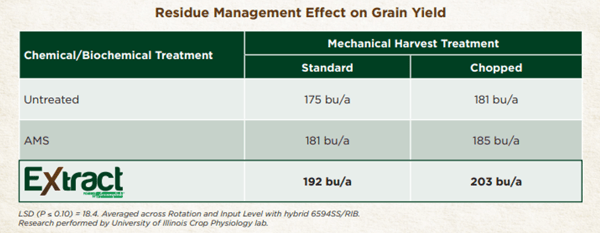
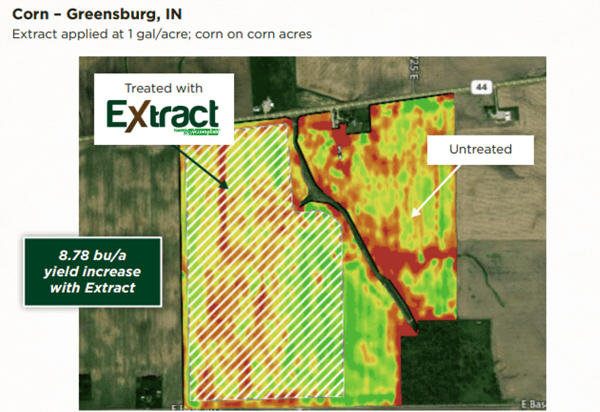
When you treat dry fertilizer with TITAN XC, the average yield response in corn is just over 10 bushels per acre, and the average yield response in soybeans is four bushels. So the economics are very consistent. TITAN XC proves itself again and again.
Dennis - WITY Radio: Tell folks how EXTRACT works.
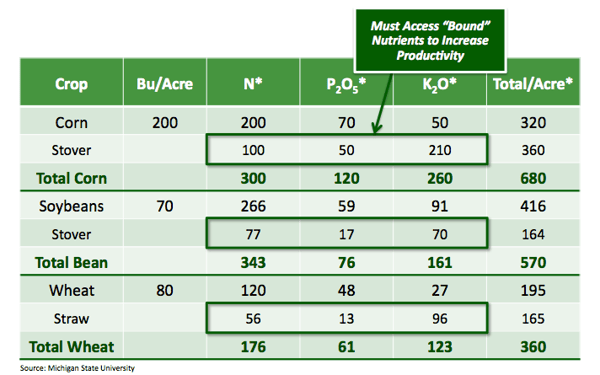
Scott - Agricen: EXTRACT is a liquid product combining the power of our biochemistry components and ammonium thiosulfate. We created it to accelerate nutrient mineralization and release in the soil—release of those nutrients that are already there, perhaps bound to the soil colloid—and also to enhance crop residue breakdown.
If we are applying EXTRACT in a broadcast application with a fall herbicide or in the spring with a broadcast application of a pre herbicide, we're able to increase the mineralization or release of nutrients in the soil while also, if it's in a minimum till situation, enhancing the breakdown of crop residue and getting that residue into more of a plant-available form more quickly.
Initially EXTRACT was targeted more towards the corn acre. We've had great success with it on corn, but as time has passed, we probably treat almost as many acres of soybeans with EXTRACT as we do corn.
Dennis - WITY Radio: When I look at data on TITAN XC and EXTRACT, I see a lot of the third-party and university data from Illinois.
Scott - Agricen: We’ve worked with the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign since 2012, and have done trials with Purdue and many other institutions as well as on-farm split-field trials where we can evaluate how the technology performs in a range of conditions. Whether we're talking about EXTRACT as a broadcast application or TITAN XC impregnated on dry fertilizer, those yield results have been pretty consistent.
TITAN XC and EXTRACT are available from Nutrien Ag Solutions.
This interview was edited for length and clarity. You can listen to the interview below or on Agricen's YouTube channel.



![[Interview] Every Dollar Counts on the Farm](https://blog.agricen.com/hubfs/Interview-every-dollar-counts.jpg)

 Jason Jaggers is a third-generation corn and soybean farmer in Wyanet, Illinois. When it comes to getting advice from his
Jason Jaggers is a third-generation corn and soybean farmer in Wyanet, Illinois. When it comes to getting advice from his 





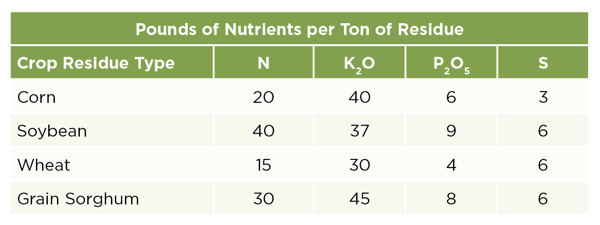
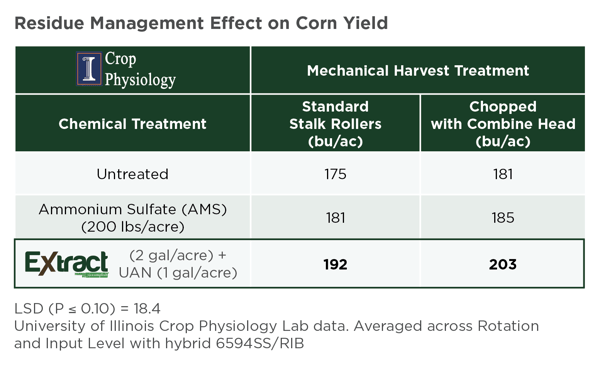 The value of
The value of 





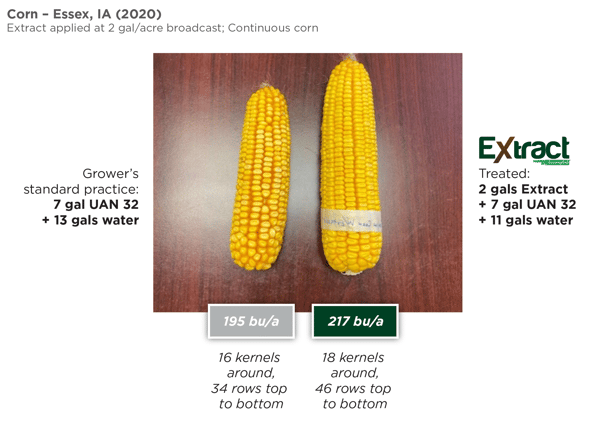
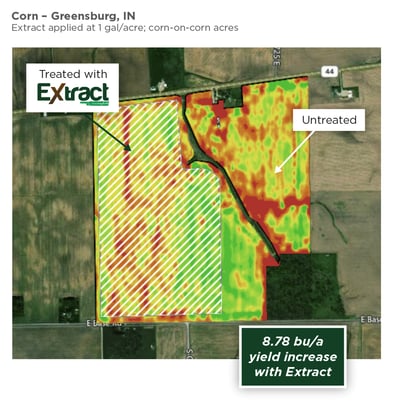
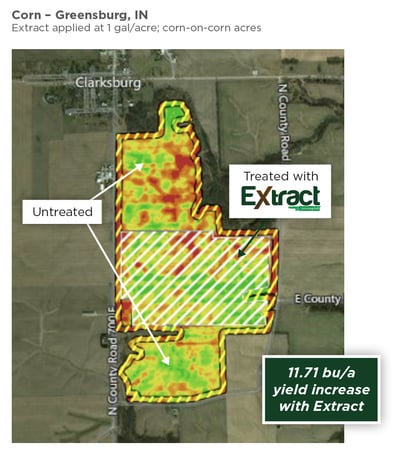

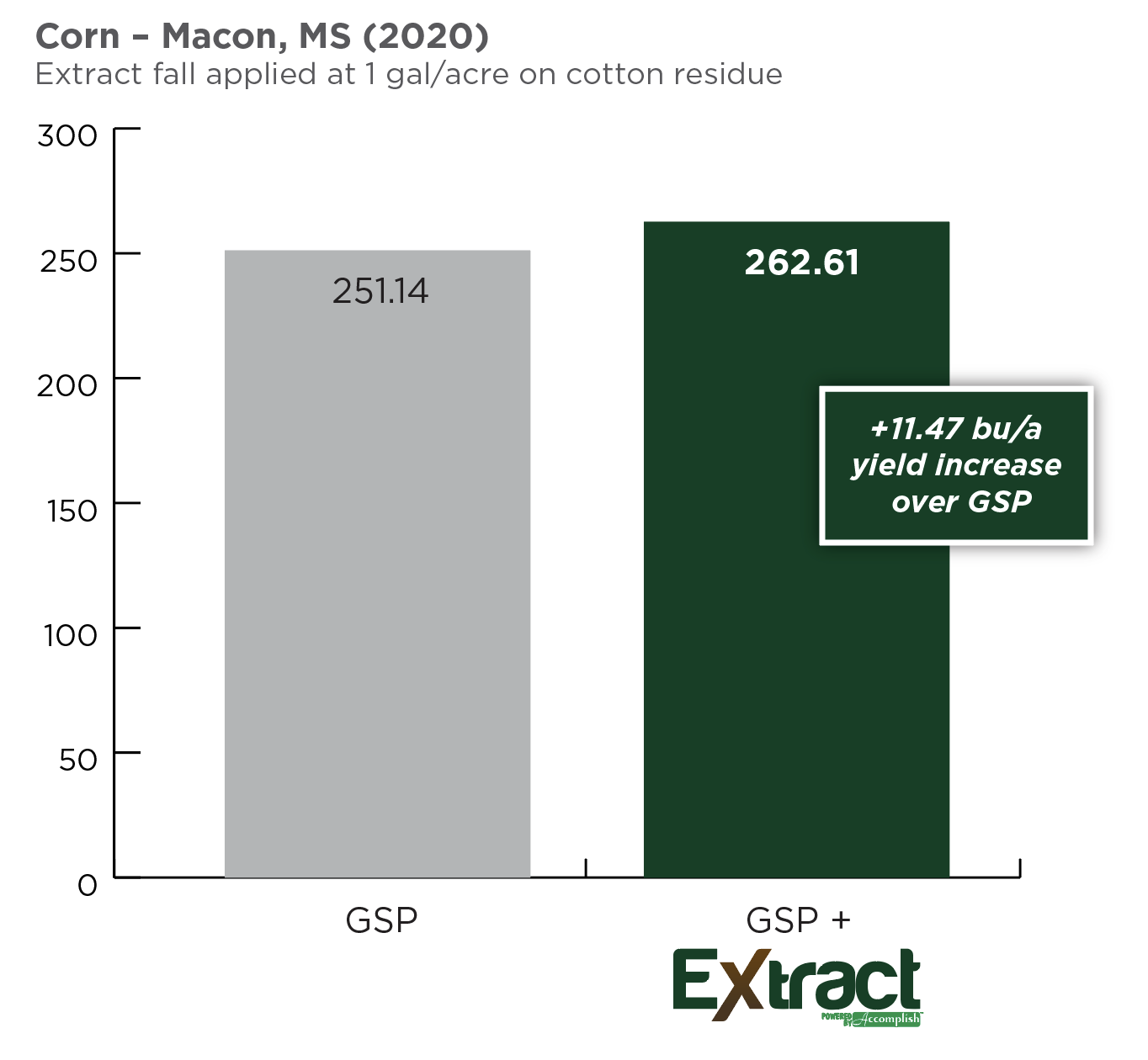
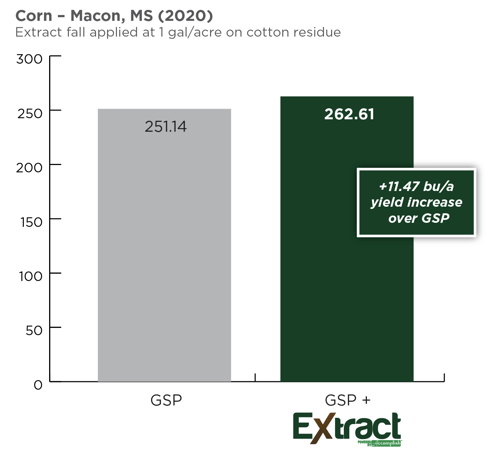
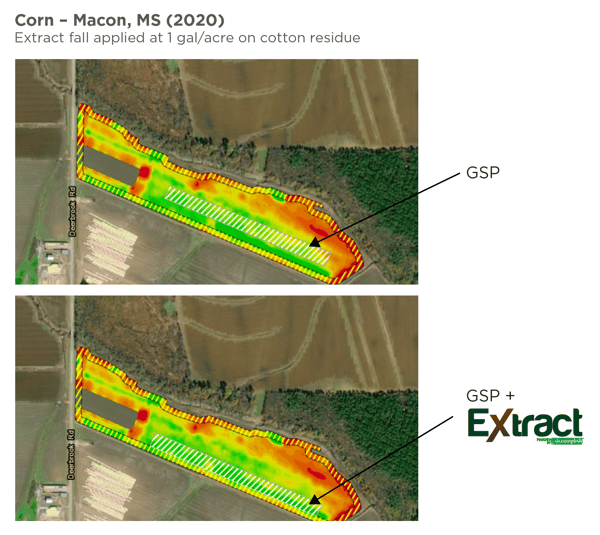


 Already a busy period, harvest is also the time for growers to begin planning for next season's crop. Fall planning can be critical to having a less stressful planting season in the spring. Incorporating
Already a busy period, harvest is also the time for growers to begin planning for next season's crop. Fall planning can be critical to having a less stressful planting season in the spring. Incorporating