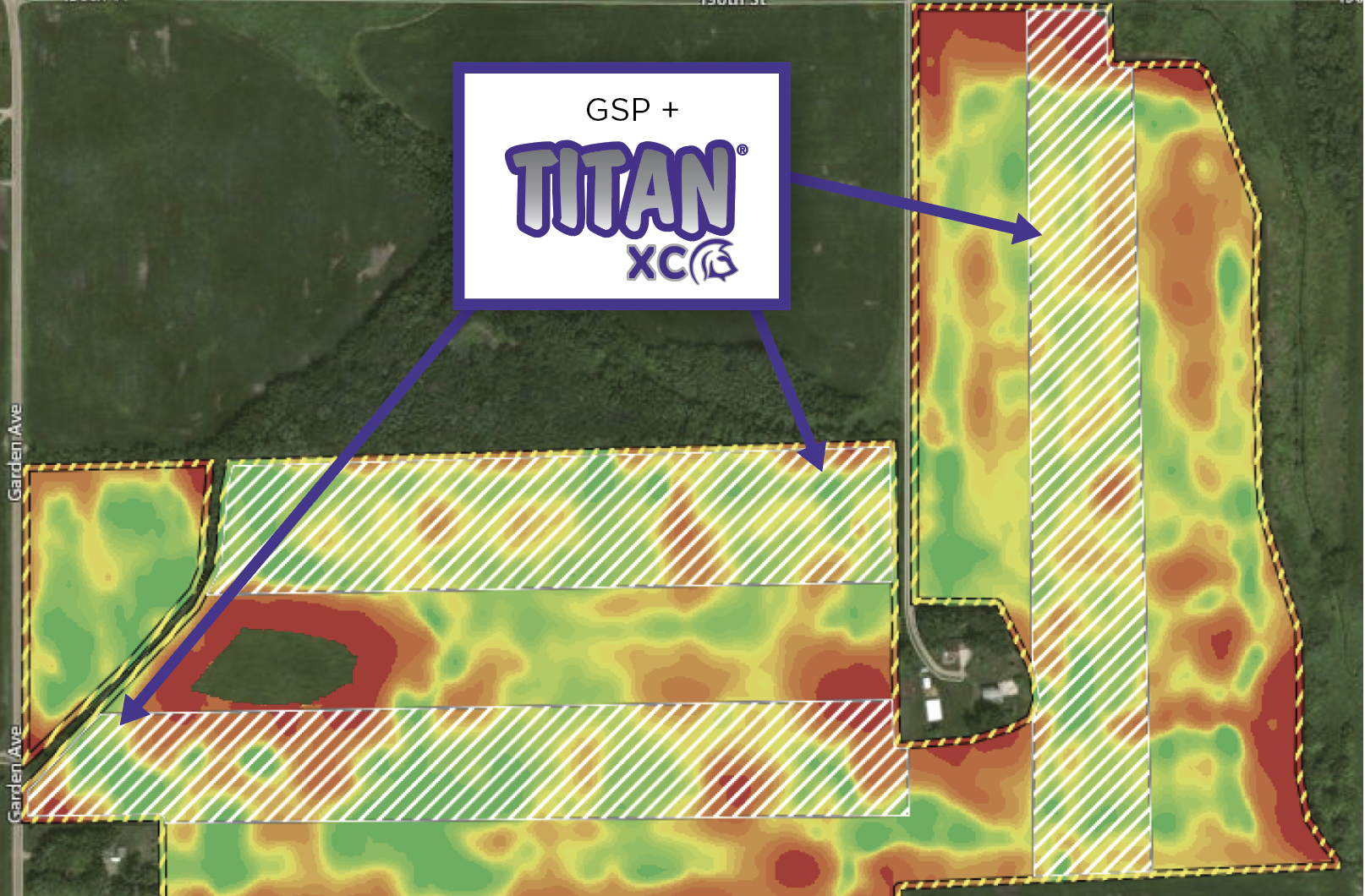
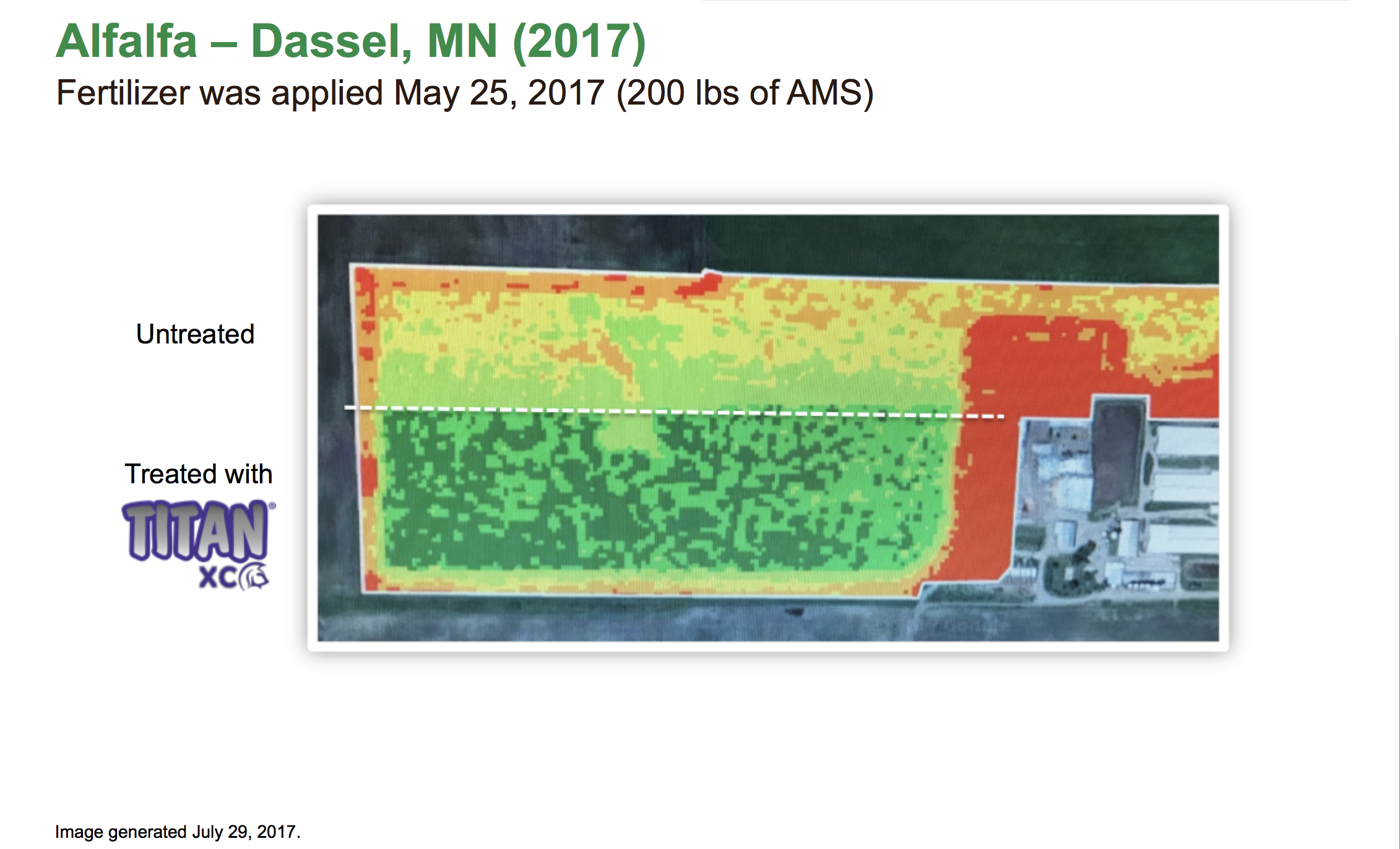
By Jeremiah Butler, Agricen
Early in the summer of 2023, widespread nutrient deficiencies were observed in the Corn Belt, particularly potassium (K) deficiency in corn. Due in large part to drier-than-average early season growing conditions, abiotic stress—or stress from environmental conditions—was more prevalent, impacting crop physiological development and reducing nutrient uptake during a critical phase.
Beginning in mid-June, a number of crop consultants were reporting an interesting phenomenon. Corn fields treated with a foliar application of TERRAMAR in the V3-V7 growth stage visually appeared to be healthier and were not exhibiting the same level of K deficiency symptoms as untreated corn.
As a result of these observations, trials were conducted on later-planted corn in Minnesota and Michigan, and on a soybean field in Indiana to evaluate the impact of a V4 application of TERRAMAR on nutrient uptake and abiotic stress reduction. Corn nutrient demand significantly increases after the V4 window to produce a healthy, high-yielding crop.
In the Minnesota trial, a foliar application of TERRAMAR (1 quart/acre) was made at V4, followed by rigorous tissue sampling to determine nutrient uptake levels of treated versus untreated plants. A total of 135 tissue samples were taken at the V9 growth stage (10 days after application) hourly over a 12-hour period (7 am to 7 pm). In addition, leaf surface temperature readings of treated and untreated plants were taken to evaluate canopy temperatures. Higher ambient air temperatures during the trial period were an indication that the corn crop was experiencing moderate heat stress.
Compared to the untreated corn, TERRAMAR increased the uptake of the majority of nutrients into the corn leaf tissue (Fig. 1). Potassium uptake was particularly notable, showing a 38% increase compared to the untreated corn.
Fig. 1. Percent increase in micro- and macronutrients in corn tissue with TERRAMAR treatment versus untreated. Samples taken 10 days after foliar application of TERRAMAR.
Leaf canopy temperature was also notably reduced in corn that had been sprayed with TERRAMAR compared to the untreated corn (Fig. 2). Lower leaf temperatures indicate that the plants were under less stress and were therefore able to more efficiently perform physiologic functions such as transpiration and photosynthesis.
 Fig. 2. Tissue temperature in the leaf canopy of corn plants treated with TERRAMAR versus untreated. Temperatures taken using thermal camera 10 days after foliar application of TERRAMAR.
Fig. 2. Tissue temperature in the leaf canopy of corn plants treated with TERRAMAR versus untreated. Temperatures taken using thermal camera 10 days after foliar application of TERRAMAR.
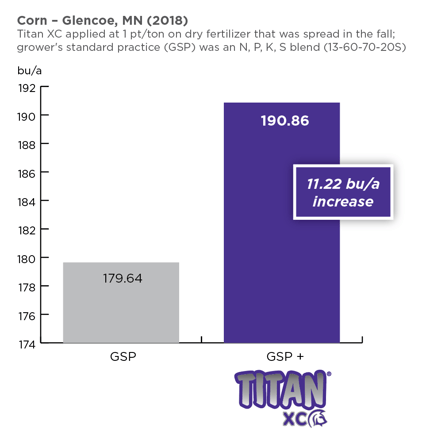
At harvest, the TERRAMAR treatment was associated with a yield advantage of +11.2 bushels/acre compared to the untreated corn (165.8 bu/a vs 154.6 bu/a, respectively).
These results are in line with prior research demonstrating TERRAMAR’s consistency in reducing stress from abiotic factors (e.g., heat, drought, salinity, wind, hail and wet environments) at any given time in the growing season following a foliar application.
While stress mitigation significantly contributes to the product’s performance, more recent research indicates that a foliar application of TERRAMAR also increases nutrient uptake (documented by leaf tissue tests in both stressed and non-stressed environments), nitrate assimilation, carbon fixation, and photosynthetic capacity. These benefits add value by providing more efficient nutrient uptake during the crop’s critical demand windows.
Every growing season creates a different set of challenges, but some things remain constant. Globally, 50% to 70% of crop yield is lost to abiotic stress factors. Taking measures to reduce the impact of abiotic stress and increase nutrient uptake throughout the growing season with new technologies like TERRAMAR provides growers a fighting chance to add more to their bottom line across a range of crops.
Learn more about TERRAMAR by accessing the Minnesota corn trial bulletin.



![[Corn Trial] Lower Canopy Temperatures & Greater Nutrient Uptake with TERRAMAR](https://blog.agricen.com/hubfs/Terramar-tissue-samples-1200px.jpg)

![[Interview] Addressing Weather-Induced Crop Stress](https://blog.agricen.com/hubfs/Interview-weather-stress.jpg)
 As growers finish putting this year’s crop in the ground, Agricen’s Scott Lay spoke with WITY Radio’s Dennis Michelsen about
As growers finish putting this year’s crop in the ground, Agricen’s Scott Lay spoke with WITY Radio’s Dennis Michelsen about 

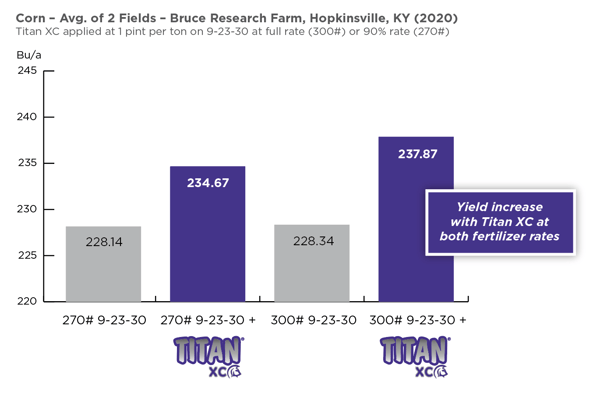


 Many agricultural areas across the United States are facing weather-related challenges, but there are still opportunities to make the most
Many agricultural areas across the United States are facing weather-related challenges, but there are still opportunities to make the most 
















 Fifth-generation farmer, Dave Kolb, of Kolb Farms near Paynesville, Minnesota, is one of 11 children who grew up working on a dairy farm with his siblings and parents. The Kolbs have been in this area since their ancestors arrived to homestead in 1861.
Fifth-generation farmer, Dave Kolb, of Kolb Farms near Paynesville, Minnesota, is one of 11 children who grew up working on a dairy farm with his siblings and parents. The Kolbs have been in this area since their ancestors arrived to homestead in 1861.



 In 2018, no fewer than five national winners and seven state winners of the
In 2018, no fewer than five national winners and seven state winners of the  Don has been entering the NCGA Corn Yield Contest since 2003, when he noticed that he was already achieving yields comparable to the growers who were winning the contest. He has been the Michigan high yield champion for nine years in a row. In both 2017 and 2018,
Don has been entering the NCGA Corn Yield Contest since 2003, when he noticed that he was already achieving yields comparable to the growers who were winning the contest. He has been the Michigan high yield champion for nine years in a row. In both 2017 and 2018,  Kevin and Shawn have been entering the NCGA Corn Yield Contest since 2007, winning 12 national titles in the non-irrigated division. Both Kevin and Shawn have had
Kevin and Shawn have been entering the NCGA Corn Yield Contest since 2007, winning 12 national titles in the non-irrigated division. Both Kevin and Shawn have had