 With planters running soon, Agricen's Scott Lay spoke with WITY Radio about utilizing Extract PBA and Accomplish MAX in the spring to minimize early season challenges related to nutrient availability and weather-related stress.
With planters running soon, Agricen's Scott Lay spoke with WITY Radio about utilizing Extract PBA and Accomplish MAX in the spring to minimize early season challenges related to nutrient availability and weather-related stress.
Dennis - WITY Radio: It has been an incredibly mild winter, but Mother Nature likes to change things up and throw a lot of stress our way, and that’s what the products from Agricen are so good at. It’s really a simple concept: Draw out more nutrients and help with the stress.
Scott - Agricen: That’s the essence of it. If you can’t minimize challenges with regard to weather-related stresses or the challenges that soil profiles present in terms of allowing plants to access nutrients, you’re not going to maximize your return.
Dennis - WITY Radio: Talk a little bit about your Extract product.
Scott - Agricen: We designed Extract for the farmer who does not utilize liquid in-furrow starter applications but wants to get that starter-like effect. It is applied in pre-plant broadcast applications with herbicide or liquid fertilizer.
The intent is really simple. We’re looking to increase the mineralization of nutrients that are already in the soil profile and release nutrients (phosphorus and potassium in particular) that are bound to that soil colloid.
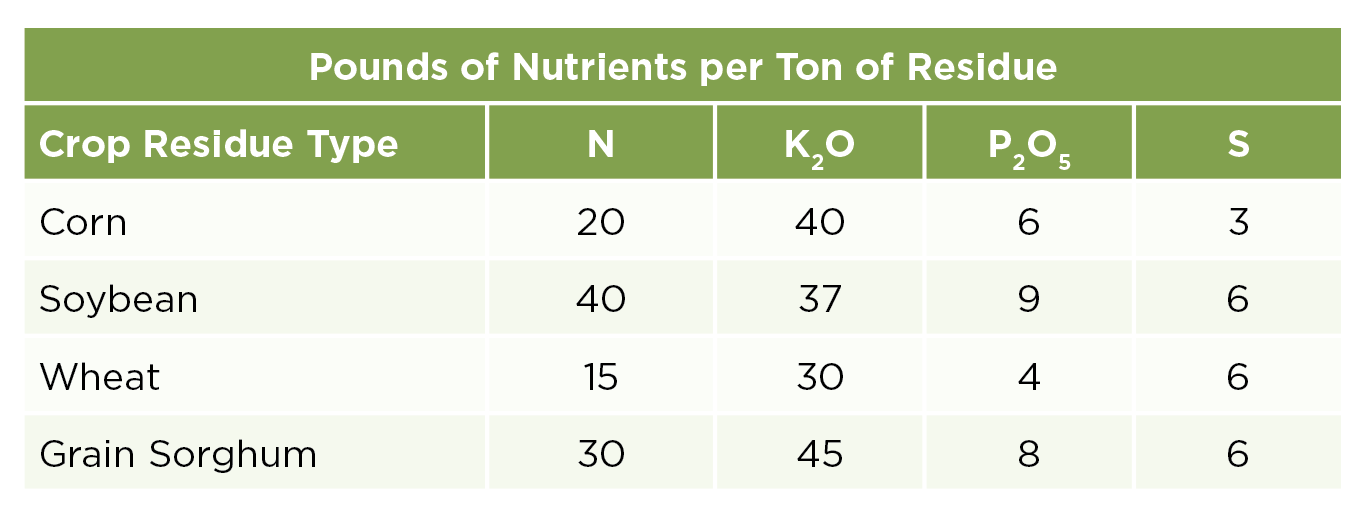
There are a lot of dollars’ worth of nutrients already in the soil profile. If we can accelerate the release of nutrients that the farmer has already paid for and put more in the plant, we’ve got a better chance for yield.
Dennis - WITY Radio: Soil tests that you have done show more available nitrogen not only in the 0- to 8-inch part of the soil profile, but way down deep at that 8- to 24-inch level. Those soil tests don’t lie...that means the product is working.
Scott - Agricen: We have University of Nebraska data to substantiate that we’re increasing both ammonium and nitrate levels in the soil. We’re increasing the amount of available nitrates at 0-8 inches by about 10% and at 8-24 inches by 15-20%. For a corn crop, that’s where the business takes place in the months of June, July and August when the plant is stretching for nutrients, so that’s a good transaction for that corn plant.
Dennis - WITY Radio: Tell us a little about the Accomplish MAX product.
Scott - Agricen: Accomplish MAX is applied with liquid in-furrow starter fertilizers. It’s not fertility, but it’s used as a companion product to liquid starters. There are two principles behind Accomplish MAX. One is to release more nutrients in the furrow, in close proximity to that planted seed. The second dimension is stress reduction. What that translates to is quicker emergence, particularly in times of cooler soil conditions which we often see during planting time.
Dennis - WITY Radio: These products are tested not only in the greenhouse environment but also in the real world in field trials.
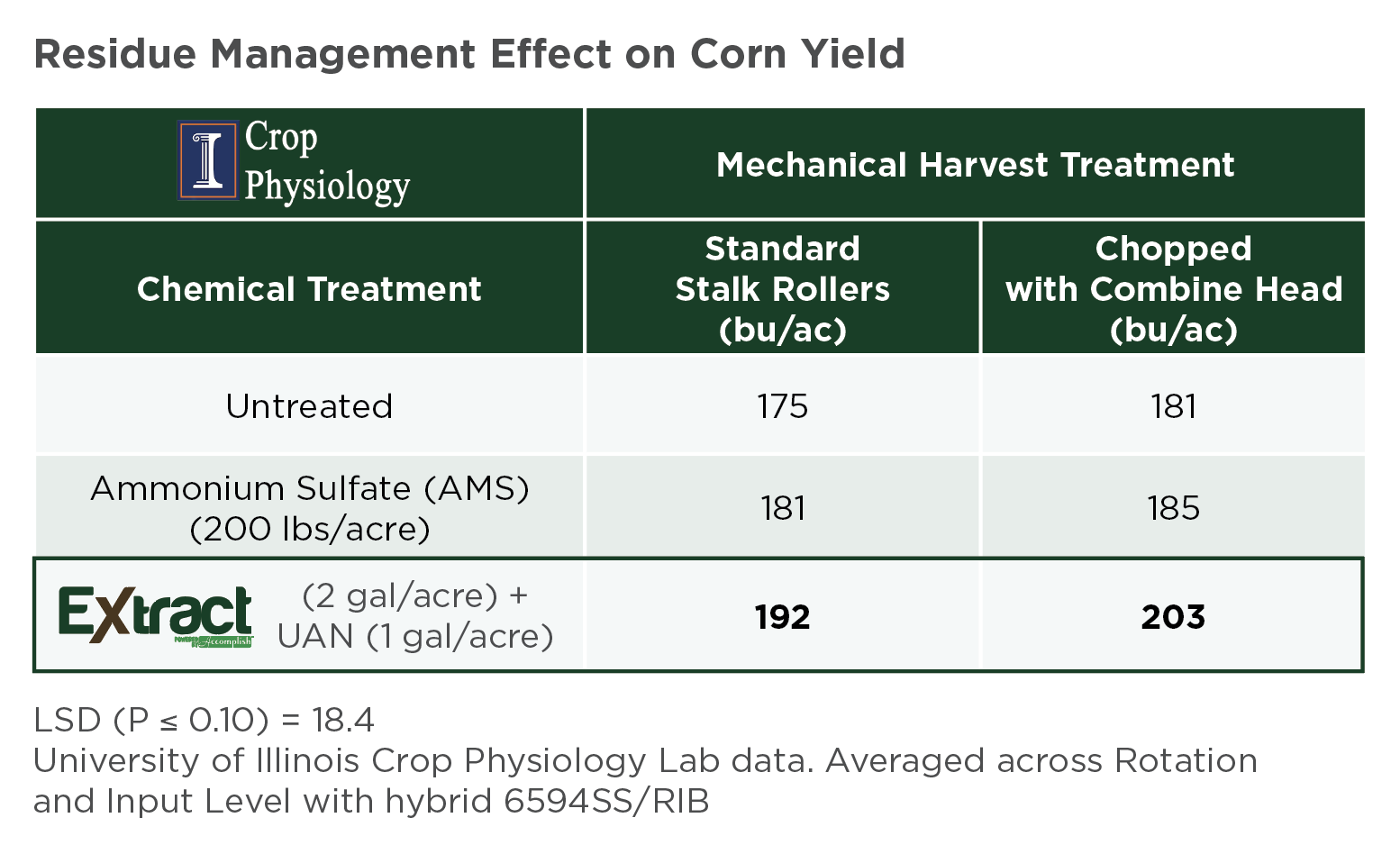
Scott - Agricen: Whether you’re in Illinois, the middle of Nebraska or southern Georgia, Accomplish MAX provides a high level of consistency regardless of crop. On average, we see about a 7 to 9-bushel response in corn and, while starter fertilizers are not as common in soybean, we still see a 4 to 5-bushel yield response. That's not just in replicated university trials, but also in real, on-farm, side-by-side trials that our customers provide for us.
Dennis - WITY Radio: And that provides customers with the return on investment they are looking for.
Accomplish MAX and Extract are available from Nutrien Ag Solutions.
This interview was edited for length and clarity. You can listen to the interview below or on Agricen's YouTube channel.
Learn more about Accomplish MAX, Extract PBA, and other innovative products by downloading the Sustainable Plant Health Technology Overview.





![[Watch] Early Season Opportunities to Enhance Plant Nutrition & Health](https://www.agricen.com/hubfs/Early-season-opp-watch-now.jpg)
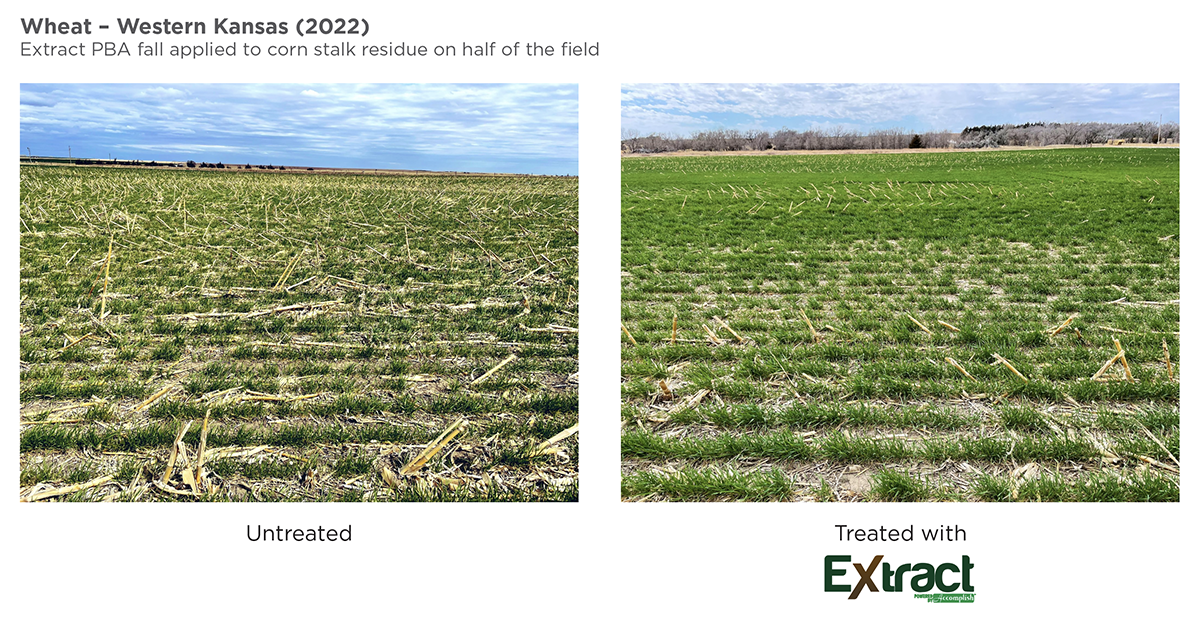





 The value of
The value of 









 As growers start crop planning for the upcoming season, where do fertilizer enhancers fit in?
As growers start crop planning for the upcoming season, where do fertilizer enhancers fit in? 


